

Modules
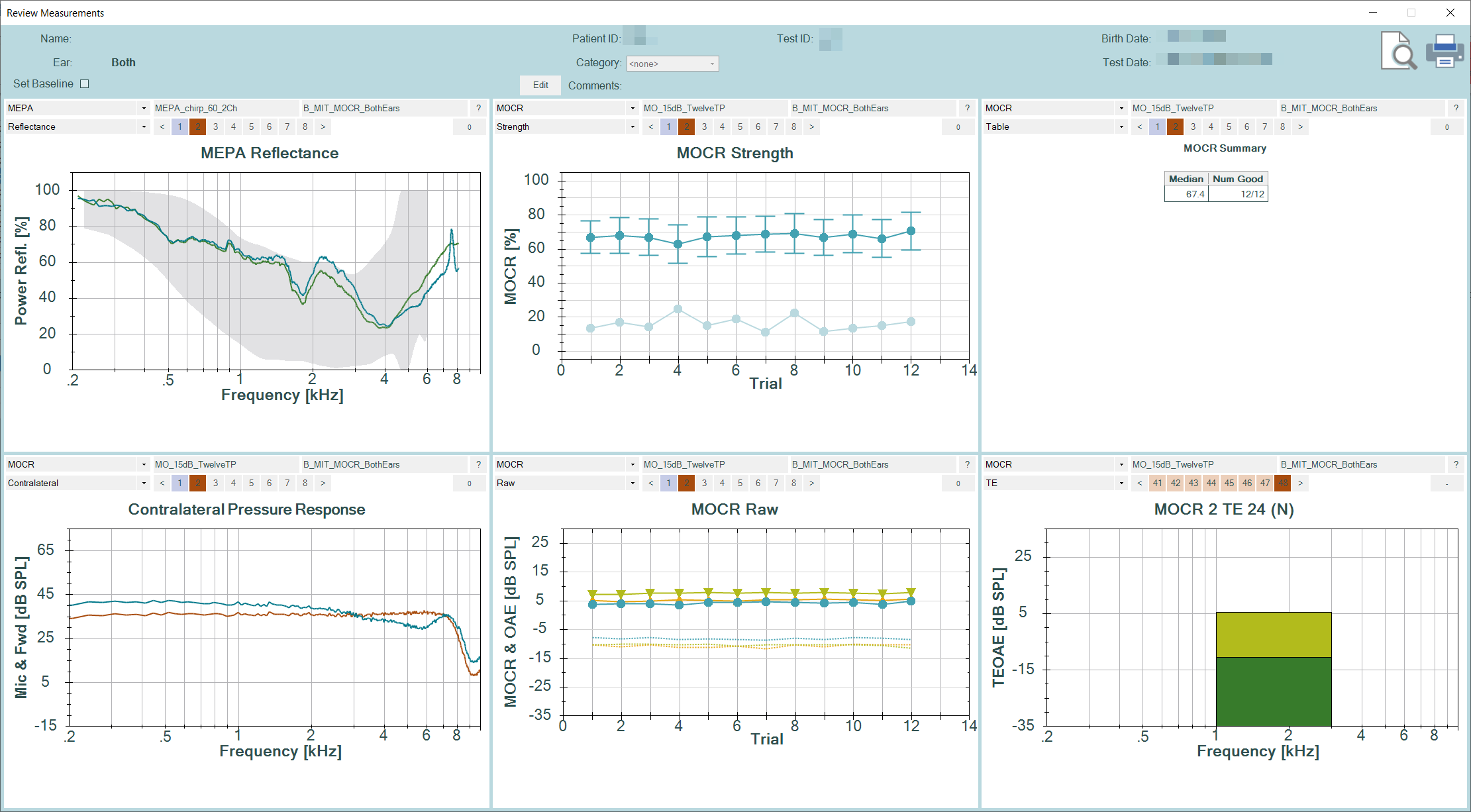
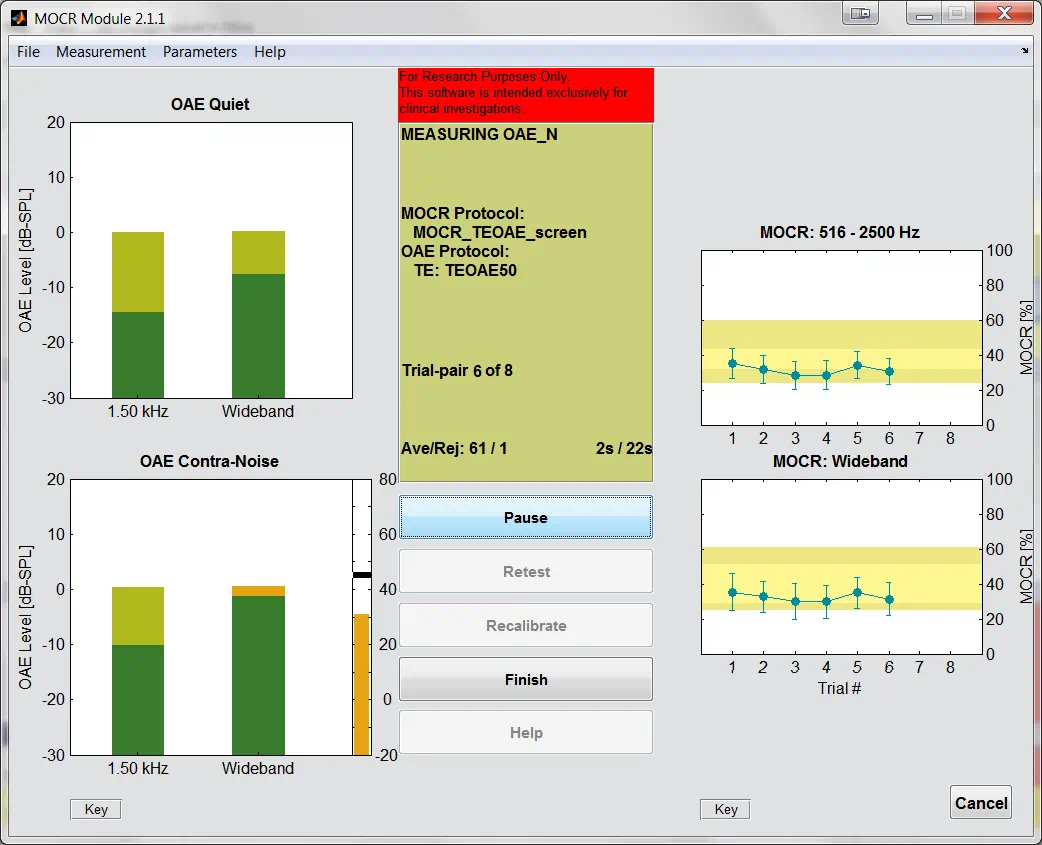
MOCR
MOCR on OtoStat 3 binaural
The binaural OtoStat system brings you a purpose-built system for testing the contralateral medial olivocochlear reflex (MOCR) with TEOAEs.
- Real-time MOCR displays.
- Use test sequences to test each ear with one click.
- User peer-reviewed published protocols, or create your own.
- Each ear probe is calibrated in situ, with the option of forward pressure level.
- Detailed data export allows for further analysis.
- Use click or chirp TEOAE stimuli in linear or non-linear mode.
- Broadband contralateral elicitor.
MOCR on HearID
The HearID system may be extended with additional hardware to test contralateral MOCR with TEOAEs or SFOAEs.
- Real-time MOCR displays.
- User peer-reviewed published protocols, or create your own.
- Test ear probe is calibrated in situ, contralateral probe is calibrated in a coupler.
- Detailed data export allows for further analysis.
- Highly customizable TEOAE and SFOAE protocols.
- Broadband or tonal contralateral elicitor.
HearID CAS add-on
Also available for the HearID TE and SF Modules for research users is a contralateral elicitor add-on (HearID MOCR module customers get this add-on for free).
The add-on generates digital broad-band noise or a tone, synchronizes the output with the TEOAE or SFOAE measurement (including programmable on and offset delays), and automatically saves the data files with a common file prefix. The benefit to using the add-on is that test sequences can be highly customized (ie arbitrary sequences of Quiet and Noise trials), but there is no real-time display of the MOCR results or any data analysis. This add-on is software only - a suitable sound card and calibrated earphone must be purchased or acquired separately.
Resources
Manuals
Further Reading
A Clinically Viable Medial Olivocochlear Reflex Assay Using Transient-Evoked Otoacoustic Emissions. by Lapsley Miller, J. A., Reed, C. M., Marshall, L., Perez, Z. D., and Villabona, T. (2023). Ear Hear., Online Ahead of Print.
Marshall, L., Lapsley Miller, J. A., Guinan, J. J., Shera, C. A., Reed, C. M., Perez, Z. D., Delhorne, L. A., and Boege, P. (2014). "Otoacoustic-emission-based medial-olivocochlear reflex assays for humans," J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 136, 2697-2713.
Lapsley Miller, J. A., Marshall, L., Reed, C. M., Perez, Z. D., and Villabona, T. (2021). Refining the procedures for medial-olivocochlear reflex (MOCR) assays: decreasing the contralateral noise reset time below 10 seconds can affect subsequent transient-evoked otoacoustic emission (TEOAE) measurements (NSMRL Technical Report No. 1344). Groton, CT: Naval Submarine Medical Research Laboratory.
Lapsley Miller, J. A., Marshall, L., Reed, C. M., and Villabona, T. (2021). Effects of stopping rules, stimulus levels, and ear laterality on transient-evoked otoacoustic emission (TEOAE)-based assays of the medial-olivocochlear reflex (MOCR) (NSMRL Technical Report No. 1346). Groton, CT: Naval Submarine Medical Research Laboratory.
Lapsley Miller, J. A., Marshall, L., Reed, C. M., and Perez, Z. D. (2021). Otoacoustic Emission (OAE) Based Assays of the Medial Olivocochlear Reflex (MOCR): Ensuring the OAE Stimulus Does Not Cause a Confounding MOCR (NSMRL Technical Report No. 1345). Groton, CT: Naval Submarine Medical Research Laboratory.